The braking system is a critical part of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control. But have you ever wondered about all the components that make up this system? Let’s take a closer look at the key parts of a brake system.
The braking system of a vehicle consists of various essential components, including the brake pads, calipers, discs, master cylinder, and brake lines. Each of these components works together to ensure effective braking performance.
Understanding the individual parts of a braking system is essential for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance or purchasing automotive parts. Let’s explore these components in more detail to see how they contribute to the overall braking performance.

What are the components of the braking system?
When we think of a braking system, we often just think about the brake pads1 and the pedal2, but the system is much more complex. Let’s explore all the components that come together to make a braking system function properly.
The braking system comprises several key components: brake pads3, calipers, brake discs (or rotors), master cylinder, brake fluid, and brake lines. These parts work together to convert the vehicle's kinetic energy into heat energy, stopping the vehicle safely.
A vehicle’s braking system is designed to be highly efficient and responsive, relying on several components that work together. Let’s break down each part’s role in the process:
| Component | Function | Material | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brake Pads | Pressed against the brake disc to create friction, slowing down the vehicle | Semi-metallic, Ceramic | Worn pads, uneven wear, glazing |
| Calipers | Houses the pistons that apply pressure to the brake pads, pushing them against the rotor | Aluminum, Steel | Leaking seals, sticking pistons, warping |
| Brake Discs | Rotating component that the brake pads press against to create the necessary friction | Cast iron, Carbon Fiber | Warping, cracking, uneven wear |
| Master Cylinder | Converts the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure to activate the brakes | Cast iron, Aluminum | Leaks, loss of hydraulic pressure, damaged seals |
| Brake Fluid | Transports hydraulic pressure throughout the brake lines and calipers | DOT fluid, Mineral oil | Contaminated fluid, moisture absorption, low fluid levels |
| Brake Lines | Transports brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers | Stainless steel, Rubber | Leaks, ruptures, corrosion |
The brake pads are pressed against the brake discs or rotors to create friction, which slows down the vehicle. These pads are essential for the braking process as they generate the necessary friction to bring the vehicle to a stop.
The brake calipers play a crucial role in the process by clamping the brake pads onto the brake discs. The calipers house the pistons that apply pressure to the pads, ensuring that enough force is applied to slow down the vehicle. Calipers are typically made from metal, and their design ensures that the pressure applied to the brake pads is consistent and effective.
The brake discs (or rotors) are the flat, circular metal components that the brake pads press against. As the pads create friction on the discs, they slow down the vehicle’s wheels. Brake discs need to be durable and heat-resistant because of the high temperatures generated during braking. Over time, these discs can wear down, requiring replacement to maintain optimal braking performance.
The master cylinder is another essential component that controls the brake fluid. It takes the force from the brake pedal and converts it into hydraulic pressure, which is then transmitted through the brake lines to the brake calipers. This hydraulic system is what allows for smooth, effective braking.
Brake fluid is essential for transferring this pressure throughout the braking system. It needs to be regularly checked and replaced to ensure that the system functions correctly. Lastly, the brake lines are responsible for carrying brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers, making sure that pressure is distributed evenly across all parts of the system.
In summary, the braking system is made up of brake pads, calipers, brake discs, master cylinders, brake fluid, and brake lines, all of which work together to bring a vehicle to a stop safely and efficiently.

What is the breakdown of a brake caliper?
The brake caliper4 is one of the most important components of the braking system, yet its structure and function are often misunderstood. What exactly is inside a brake caliper, and how does it contribute to the braking process?
The brake caliper is made up of several key components: the caliper housing5, pistons6, and seals7. It applies pressure to the brake pads, forcing them to contact the brake disc and create the friction needed to stop the vehicle.
The brake caliper plays a crucial role in the braking process. Let’s break down its components in more detail:
| Component | Function | Material | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caliper Housing | Encloses all components and ensures their proper alignment and function | Cast iron, Aluminum | Cracks, corrosion |
| Pistons | Pushes the brake pads against the rotor to generate friction | Steel, Aluminum, Plastic | Sticking, leaking, uneven pressure distribution |
| Seals | Prevents brake fluid leakage and keeps debris out of the caliper | Rubber, Silicone | Leaks, wear, contamination |
| Bleeder Valve | Releases air or moisture from the brake system | Steel, Rubber | Blockage, failure to release air |
Inside the caliper housing, you'll find the pistons. These pistons are typically made of steel, aluminum, or plastic, and they play a vital role in applying pressure to the brake pads. When brake fluid enters the caliper, it pushes the pistons outward, causing them to press the brake pads against the brake discs. This contact generates the necessary friction to slow down or stop the vehicle.
The number of pistons in a caliper can vary. Some calipers have a single piston, while others have multiple pistons (often called multi-piston calipers). Multi-piston calipers are typically used for high-performance vehicles as they provide more even pressure on the brake pads, resulting in better braking performance.
Seals are another important feature of the brake caliper. These rubber seals prevent brake fluid from leaking and ensure that the system maintains proper hydraulic pressure. Without seals, the caliper would fail to operate correctly, and the brake system would lose its ability to stop the vehicle efficiently.
The bleeder valve in the caliper is another important part. This valve allows you to release any trapped air or moisture that may have entered the brake system. Trapped air can cause inconsistent braking performance, so it's essential to ensure that the brake fluid is free from air bubbles.
A well-maintained brake caliper is essential for overall braking performance. If any of the components inside the caliper become damaged or wear down, it can lead to inefficient braking, uneven wear on the brake pads, or even a complete failure of the braking system. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial to ensuring that the brake calipers continue to function optimally.

What is the break-in procedure for brakes?
Once you've installed new brake pads8 and components, it’s critical to properly break in9 the system to ensure maximum performance and longevity. But what does the brake-in procedure entail, and why is it so important?
The break-in procedure, also known as bedding in10, involves gradually applying the brakes in a controlled manner to help the pads and rotors wear in evenly. This process ensures optimal contact between the pads and discs for better braking performance.
The break-in procedure, or bedding-in process, is critical for ensuring that the brake pads and rotors wear evenly and provide the best possible performance. Here’s how the procedure works and why it’s so important:
| Step | Action | Time/Distance | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Brake Application | Gradually apply brakes at low speeds to create light contact | 1-2 minutes | Allow pads and rotors to make initial contact and wear evenly |
| Moderate Braking | Apply the brakes more firmly but still avoid full stops | 5-10 minutes | Increase friction and heat to help pad material transfer to the rotor surface |
| Cooling Period | Allow the brakes to cool between braking sessions | 5-10 minutes | Prevent overheating and rotor warping |
| Heavy Braking | Perform moderate braking from higher speeds, avoid hard stops | 200-300 miles | Ensure the pads and rotors are fully bedded and working optimally |
The purpose of bedding in new brakes is to transfer a thin layer of brake pad material onto the surface of the brake rotor. This process helps ensure that the pads and rotors make full, even contact with each other, which increases the effectiveness of the braking system.
The initial step involves applying the brakes lightly and gradually increasing pressure. It’s essential to avoid hard or sudden stops in the first 50 to 100 miles, as this can cause uneven wear and reduce the brake pads’ lifespan. Instead, apply the brakes gently to heat them up and allow the materials to transfer evenly onto the rotor surface.
After several initial brake applications, you should start performing more moderate braking, but avoid locking up the brakes or coming to a complete stop. During this phase, the brake pads continue to wear in and adapt to the surface of the rotors. Allow the brakes to cool periodically to prevent them from overheating.
Finally, after completing the initial bedding-in phase, you can begin to brake more aggressively, but still avoid full stops unless necessary. The entire break-in period typically lasts for the first 200-300 miles, during which the pads and rotors continue to settle into each other for maximum efficiency.
By properly breaking in the brakes, you ensure that your new parts will deliver optimal performance and have a longer lifespan. A proper bedding-in procedure is crucial for achieving smooth, reliable braking.
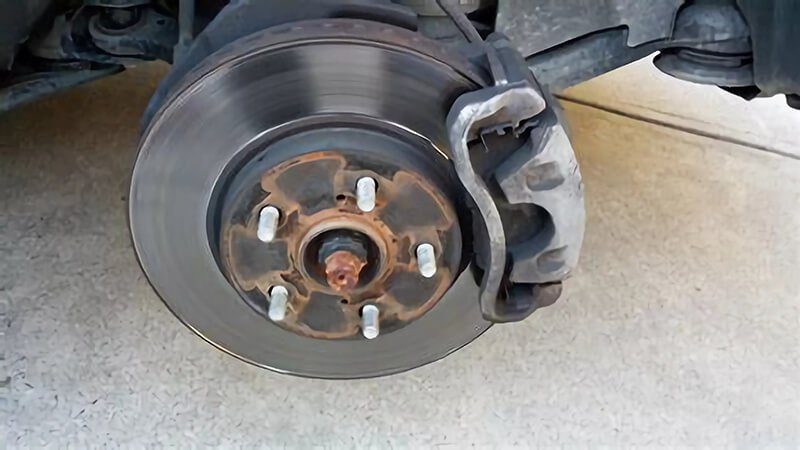

What makes up a brake system?
We've explored individual components of the braking system11, but what is the bigger picture? How do all these parts work together to stop a vehicle efficiently?
The entire brake system is a collection of interconnected components, including brake pads12, calipers, rotors, master cylinder, fluid, and lines. Together, they convert kinetic energy into heat, stopping the vehicle smoothly and reliably.
Dive deeper Paragraph: The brake system is more than just the sum of its parts. When you press the brake pedal, the entire system works in harmony to bring the vehicle to a stop. Here's a breakdown of how everything fits together:
The brake system is more than just the sum of its parts. When you press the brake pedal, the entire system works in harmony to bring the vehicle to a stop. Here's a breakdown of how everything fits together:
| Step | Component | Role in the Process |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Pressing Brake Pedal | Brake Pedal | The driver applies force to the pedal, initiating the braking process. |
| 2. Generating Hydraulic Pressure | Master Cylinder | Converts the force from the pedal into hydraulic pressure. |
| 3. Transmitting Fluid | Brake Lines and Fluid | Carry hydraulic pressure to the calipers. |
| 4. Applying Pressure | Brake Calipers and Pistons | Apply pressure to the brake pads, clamping them onto the rotor. |
| 5. Creating Friction | Brake Pads and Rotors | The pads press against the rotors, generating the friction that slows the vehicle down. |
| 6. Stopping the Vehicle | Entire Brake System | The friction between the pads and rotors converts kinetic energy into heat, stopping the vehicle. |
Each of the components works seamlessly to ensure that braking is smooth and effective. The brake pedal initiates the process, which is then converted into hydraulic pressure by the master cylinder. This pressure travels through the brake lines, activating the calipers, which apply pressure to the brake pads. These pads create friction against the brake rotors, generating the force needed to slow or stop the vehicle.
The brake system is designed to operate in a highly coordinated manner, where each part plays a critical role in ensuring effective braking. Even small malfunctions in any one component can affect the system’s performance, making regular maintenance and inspection crucial for vehicle safety.

Conclusion
The braking system is a complex assembly of parts working together to ensure the safety of a vehicle. From brake pads to calipers, master cylinders to brake lines, each component plays a critical role in providing reliable stopping power. Understanding how these components work together helps in maintaining the braking system and ensuring optimal performance. Regular inspections and proper maintenance are key to keeping the system functioning efficiently and safely.
-
This will help you understand the importance of brake pads in stopping the vehicle safely. ↩
-
This link will explain how the brake pedal interacts with other components in the braking system. ↩
-
Learn about the types of brake pads and how they impact vehicle performance. ↩
-
Understand the essential function of the brake caliper in the overall braking process. ↩
-
Learn about the caliper housing's role in providing structure and support to the caliper components. ↩
-
Discover how brake caliper pistons create the force needed to engage the brake pads. ↩
-
Find out how seals in the brake caliper prevent leaks and maintain hydraulic pressure for effective braking. ↩
-
Learn how new brake pads play a vital role during the brake-in process to ensure even wear. ↩
-
Understand the importance of properly breaking in new brake components for optimal performance and safety. ↩
-
Gain insight into the bedding-in process and its effect on the durability of brake pads and rotors. ↩
-
This will help you understand how all the components of a braking system interact to stop a vehicle. ↩
-
Learn about the brake pads’ role in converting kinetic energy into heat to safely stop the vehicle. ↩