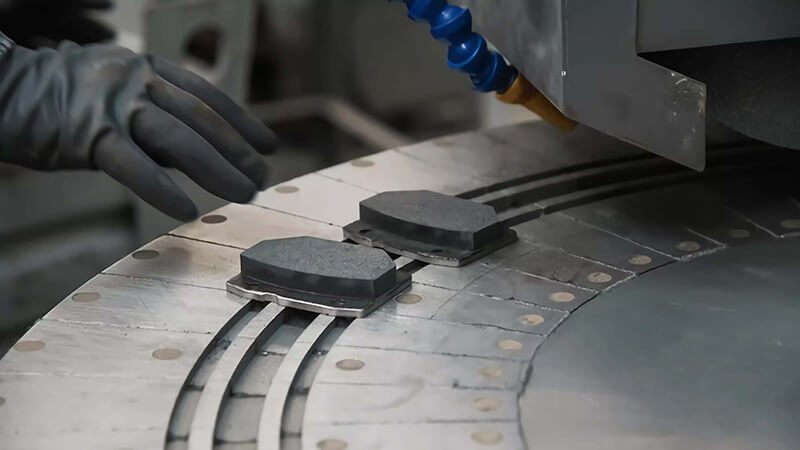
Brake auto parts are essential for ensuring a vehicle stops efficiently and safely. Understanding how these components work together is key to vehicle performance and safety. In this guide, we’ll break down the key brake parts and their functions to give you a deeper understanding of how your car stops.
Brake parts like disc brakes, drum brakes, master cylinders, and brake pads are all critical for your vehicle’s stopping power. Knowing how they function and differ can help you make informed choices for repairs and replacements.
Now that we understand the importance of braking systems, let’s dive into the specific components and their roles in ensuring the safety and performance of your vehicle.
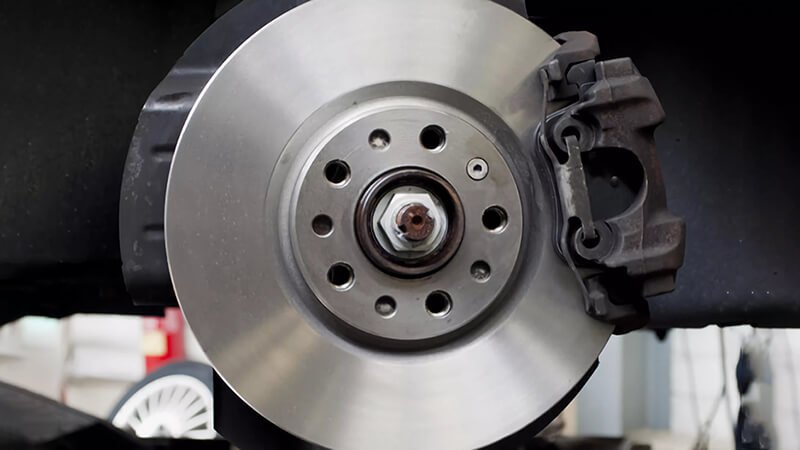

What are the differences between disc brakes and drum brakes?
Disc brakes and drum brakes are two common types of braking systems. While both serve the same basic function, they operate differently, and each has its pros and cons. Let’s break down their differences.
Disc brakes use a rotor and caliper to slow down the vehicle, while drum brakes use a set of shoes inside a drum. Disc brakes generally offer better performance, especially in wet conditions, while drum brakes are more cost-effective.
Disc and drum brakes are both essential for vehicle braking systems, yet they function in different ways and cater to different needs. Let’s explore each type more deeply to understand their mechanics and benefits.
Disc Brakes – The Modern Standard
Disc brakes are the standard in most modern vehicles due to their superior performance in a variety of conditions. A disc brake system consists of a metal rotor, which rotates with the wheel, and a caliper, which holds the brake pads. When you press the brake pedal, hydraulic force pushes the brake pads onto the rotor. The friction slows the wheel and brings the car to a stop. Disc brakes have several advantages:
- Superior heat dissipation: The flat, exposed rotor design allows for better heat management, reducing the risk of brake fade (the loss of braking power due to overheating) brake fade1.
- Consistent performance in all conditions: Disc brakes are more effective in wet conditions since water is less likely to accumulate on the exposed rotor surface. In contrast, drum brakes can retain moisture, reducing braking efficiency in the rain wet braking performance2.
- Faster stopping power: Disc brakes tend to respond more quickly, which is why they are preferred for high-performance vehicles and sports cars.
Drum Brakes – Cost-Effective but Less Efficient
Drum brakes are older technology but are still used in many vehicles, especially on the rear axles. The system consists of a cylindrical drum that rotates with the wheel and brake shoes that press against the inside of the drum when you apply pressure to the brake pedal. The friction generated between the brake shoes and the drum slows the wheel. Here’s why drum brakes are still used:
- Cost-effective: Drum brakes are less expensive to manufacture than disc brakes, making them a cost-effective solution for rear-wheel brakes cost-effective braking3.
- Better for light-duty vehicles: While disc brakes outperform drum brakes in high-performance and heavy-duty applications, drum brakes still work well in smaller, lighter vehicles that don’t require the same level of stopping power.
- More compact design: Drum brakes have a more compact design, which allows them to fit in smaller spaces, and can be a good choice in designs where space is limited.
While drum brakes continue to serve in some vehicles, especially in rear wheel and budget-friendly applications, they generally offer less performance and require more frequent maintenance compared to disc brakes.

How does the master cylinder function in the braking system?
The master cylinder is a crucial part of the braking system, as it generates the hydraulic pressure needed to activate the brakes. Without a properly functioning master cylinder, the entire braking system would fail.
The master cylinder is responsible for converting the force you apply on the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. This pressure is what activates the brake components, such as the brake pads and shoes, to stop the vehicle.
The master cylinder plays an indispensable role in the hydraulic braking system. Its primary function is to convert the mechanical force from the brake pedal into hydraulic force, allowing the brakes to activate. Let’s break down how this process works in detail.
Hydraulic Pressure and the Brake Master Cylinder
When you press the brake pedal, the force is transmitted through the brake booster, which amplifies your foot pressure. The master cylinder, located near the brake pedal, is filled with brake fluid. This fluid is essential because it acts as the medium that transfers the braking force through the system brake fluid4.
- The two main types of master cylinders: There are single and dual master cylinders. The single master cylinder is used in older vehicles, while modern vehicles use a dual master cylinder for added safety. A dual master cylinder is split into two separate circuits – one for the front brakes and one for the rear brakes. This separation ensures that if one circuit fails, the other will still function, providing some braking power dual master cylinders5.
- Creating hydraulic force: Inside the master cylinder is a piston that, when you press the brake pedal, moves forward, pushing brake fluid into the brake lines. This hydraulic force travels to the wheel cylinders or calipers at the brakes, where it forces the brake pads or shoes into contact with the braking surface (rotor or drum).
- Brake fluid: The master cylinder relies on brake fluid to transmit pressure. The fluid must be maintained at the proper level and composition to ensure safe operation. Low brake fluid levels or contaminated fluid can lead to brake failure.
The master cylinder is essential for transmitting brake pedal force into stopping power. Without it, the hydraulic system would not function, and the vehicle would be unable to stop.

What materials are commonly used for brake calipers?
Brake calipers are a key part of the braking system, clamping the brake pads onto the rotor to create the friction necessary for stopping the vehicle. The materials used for calipers affect their strength, weight, and performance.
Brake calipers are typically made from aluminum, cast iron, or carbon composite materials. Each material has its own set of benefits, such as improved performance or reduced weight.
Brake calipers are a crucial part of a vehicle’s braking system, and their material composition directly influences their performance, weight, and cost. Let’s take a deeper look into the common materials used in calipers and how they impact braking performance.
Aluminum Calipers – Lightweight and Performance-Oriented
Aluminum is the most common material used for brake calipers in performance and modern vehicles. Aluminum calipers are known for their lightweight nature and ability to dissipate heat more efficiently, both critical characteristics in high-performance braking systems.
- Lightweight: Aluminum calipers reduce the overall weight of the braking system, improving vehicle handling and fuel efficiency. This is especially important in sports cars and performance vehicles where every pound counts lightweight calipers6.
- Improved heat dissipation: The heat generated during braking must be dissipated quickly to avoid brake fade. Aluminum, being an excellent heat conductor, allows calipers to manage temperature better than other materials heat dissipation in brakes7.
- Corrosion resistance: Aluminum is resistant to rust and corrosion, which increases the longevity of the braking system. It’s especially beneficial for vehicles that are exposed to harsh conditions like rain or snow.
Cast Iron Calipers – Durable but Heavier
Cast iron calipers are traditionally used in commercial vehicles, trucks, and older car models. They offer durability and high strength, although they come with the downside of being heavier than aluminum.
- Durable and strong: Cast iron calipers are able to withstand high levels of pressure and force. They are often used in vehicles that require heavy-duty braking, like trucks or SUVs durability of cast iron8.
- Lower cost: Cast iron is cheaper to manufacture, making it a cost-effective option for budget-conscious vehicles cast iron calipers cost9.
- Heat management: While cast iron is not as efficient as aluminum in heat dissipation, it still performs well in heavy-duty applications where sustained braking is required.
Carbon Composite Calipers – The Best of Both Worlds
Carbon composite calipers are used in high-performance or racing vehicles where every aspect of braking is optimized for maximum efficiency. These calipers combine carbon fiber with a resin binder to create a lightweight and incredibly strong material.
- Super lightweight: Carbon composite calipers are incredibly light, which improves handling and braking response, particularly in high-performance cars carbon composite calipers10.
- Extreme heat resistance: The material can withstand extremely high temperatures, making it ideal for racing or situations where constant heavy braking is necessary heat resistance in carbon composite11.
- Long lifespan: The composite material resists wear and tear over time, making carbon composite calipers ideal for long-term performance.
The choice of caliper material depends on the specific needs of the vehicle. Performance cars benefit from the lightweight nature of aluminum or carbon composites, while trucks and heavy-duty vehicles rely on the durability of cast iron.
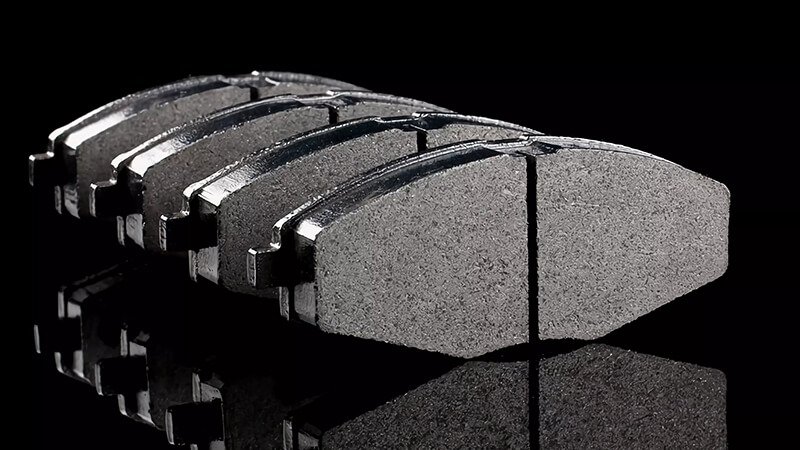

How do brake pads differ in terms of materials and performance?
Brake pads are vital for creating the friction needed to stop your vehicle. The material used in the brake pads directly impacts their performance, lifespan, and the overall braking experience.
Brake pads are made from a variety of materials, including organic, metallic, and ceramic compounds. Each type offers different performance characteristics, such as better heat resistance, noise control, or durability.
Brake pads are essential components that create the friction necessary to stop your car. The materials used in brake pads significantly influence their overall performance. Let’s take a deeper look at the different types of brake pad materials and how each affects performance.
Organic Brake Pads – Quiet and Smooth
Organic brake pads are composed of natural materials like rubber, glass, and resin. These pads are known for their quiet operation and smooth braking feel.
- Quiet operation: Organic pads produce less noise compared to metallic or ceramic pads. This makes them an excellent choice for everyday driving quiet brake pads12.
- Smooth braking feel: Organic pads provide a softer and more gradual braking response, which is ideal for city driving or lighter vehicles.
- Eco-friendly: These pads are made from natural materials, which makes them a more environmentally friendly option compared to other types.
Metallic Brake Pads – Strong and Heat-Resistant
Metallic brake pads contain metal fibers, such as steel, copper, or brass, mixed with other materials to enhance strength and heat resistance. They offer exceptional stopping power but come with some drawbacks.
- Durability and strength: Metallic pads are built to last and can handle high temperatures, making them suitable for performance or heavy-duty vehicles durability of metallic pads13.
- Better performance in heavy braking: These pads perform better in aggressive or sustained braking scenarios, such as mountain driving or towing.
- Increased noise and dust: Metallic pads can be noisier and produce more brake dust than other materials, which might require more frequent cleaning metallic pads cleaning14.
Ceramic Brake Pads – High Performance with Low Dust
Ceramic brake pads use a blend of ceramic fibers and fillers. They are known for offering a balance of performance, comfort, and longevity.
- Less dust and noise: Ceramic pads produce significantly less brake dust and are quieter than metallic pads ceramic brake pad benefits15.
- Excellent performance: They offer strong stopping power without sacrificing comfort, making them ideal for daily drivers.
- Durability: Ceramic pads are highly durable, lasting longer than organic pads and performing well under heat.
The choice of brake pad material depends on your driving needs, whether you prioritize quietness, performance, or durability.

What role does the brake booster play in the braking process?
The brake booster plays an essential role in helping you apply enough force to the brake system with minimal effort. Let’s explore how this component improves braking efficiency.
The brake booster uses vacuum or hydraulic pressure to amplify the force you apply to the brake pedal, making it easier to stop the vehicle. Without the booster, you would need to exert much more effort to activate the brakes.
The brake booster is a key component in modern vehicles, amplifying the force you apply to the brake pedal to ensure safe, efficient braking. Let’s explore how it works in greater detail.
Brake Booster Mechanism – Amplifying Pedal Force
The brake booster is a diaphragm device that uses vacuum or hydraulic pressure to assist in applying force to the brake master cylinder. Without the booster, you would need to apply significantly more effort to stop the vehicle. Here’s how it works:
- Vacuum assist: Most brake boosters operate using vacuum pressure. The vacuum is typically created by the engine and stored in a chamber. When the brake pedal is pressed, a valve inside the booster opens, allowing vacuum pressure to assist in pushing the brake master cylinder piston.
- Hydraulic assist: In heavy-duty vehicles, hydraulic brake boosters are used. Instead of vacuum, hydraulic fluid is used to amplify pedal pressure. These systems are more powerful and are typically used in trucks or larger vehicles.
- Effortless braking: The brake booster reduces the physical effort needed to stop the vehicle, making it easier to apply the right amount of pressure to the brake system without straining.
The brake booster’s function is essential for ensuring that you can stop the vehicle efficiently with minimal effort, contributing to safety and driver comfort.

Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the different components of a braking system and how they function is key to ensuring your vehicle’s safety and performance. From brake pads and calipers to the master cylinder and booster, each part plays a crucial role in providing reliable stopping power. Always prioritize quality and maintenance to ensure your braking system operates at its best.
-
Learn about brake fade and its impact on vehicle braking performance. ↩
-
Understand why disc brakes are more efficient in wet conditions compared to drum brakes. ↩
-
Find out why drum brakes are cheaper to manufacture than disc brakes. ↩
-
Learn about the role of brake fluid in the hydraulic braking system and its importance for safe braking. ↩
-
Understand the difference between single and dual master cylinders and their impact on vehicle safety. ↩
-
Discover the benefits of using lightweight brake calipers in high-performance vehicles. ↩
-
Learn how aluminum calipers improve heat dissipation in braking systems. ↩
-
Understand why cast iron is preferred for brake calipers in heavy-duty vehicles. ↩
-
Learn about the cost advantages of using cast iron for brake calipers. ↩
-
Explore the use of carbon composite brake calipers in high-performance racing vehicles. ↩
-
Discover the heat resistance properties of carbon composite brake calipers. ↩
-
Understand why organic brake pads are quieter and how they benefit everyday driving. ↩
-
Learn about the durability and strength of metallic brake pads in performance vehicles. ↩
-
Find out how to clean brake pads and manage the dust produced by metallic pads. ↩
-
Explore the benefits of ceramic brake pads and how they improve braking performance and longevity. ↩